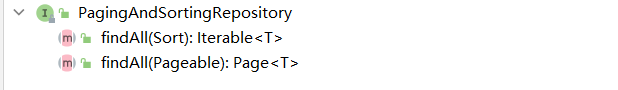【基于JPA的Repository使用详解】_jparepository 用法_Bug智造机的博客-CSDN博客
简介
Spring Data是Spring提供的操作数据的框架,Spring Data JPA是Spring Data的一个模块,通过Spring data 基于JPA标准操作数据的模块。
Spring Data的核心能力,就是基于JPA操作数据,并且可以简化操作持久层的代码。
它使用一个叫作Repository的接口类为基础,它被定义为访问底层数据模型的超级接口。而对于某种具体的数据访问操作,则在其子接口中定义。
Spring Data可以让我们只定义接口,只要遵循Spring Data的规范,就无需写实现类,不用写sql语句直接查询数据。
Repository
提供了findBy + 属性方法。
CrudRepository
继承了Repository,提供了对数据的增删改查。
PagingAndSortRepository
继承了CrudRepository,提供了对数据的分页和排序,缺点是只能对所有的数据进行分页或者排序,不能做条件判断。
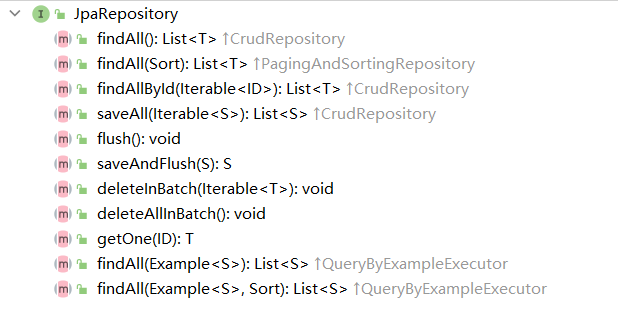
JpaRepository
继承了PagingAndSortRepository,提供开发中经常使用的接口,主要继承了PagingAndSortRepository,对返回值类型做了适配。
因为在父类接口中通常都返回迭代器,需要我们自己进行强制类型转化。而在JpaRepository中,直接返回了List。
JpaRepository查询功能
Jpa方法命名规则
JpaRepository支持接口规范方法名查询。意思是如果在接口中定义的查询方法符合它的命名规则,就可以不用写实现,目前支持的关键字如下。
| Keyword关键字 | Sample举例 | JPQL snippet片段 |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByNameAndPwd | where name= ? and pwd =? |
| Or | findByNameOrSex | where name= ? or sex=? |
| Is, Equals | findByIdEquals | where id= ? |
| Between | findByIdBetween | where id between ? and ? |
| LessThan | findByIdLessThan | where id < ? |
| LessThanEquals | findByIdLessThanEquals | where id <= ? |
| GreaterThan | findByIdGreaterThan | where id > ? |
| GreaterThanEquals | findByIdGreaterThanEquals | where id > = ? |
| After | findByIdAfter | where id > ? |
| Before | findByIdBefore | where id < ? |
| IsNull | findByNameIsNull | where name is null |
| isNotNull, NotNull | findByNameNotNull | where name is not null |
| Like | findByNameLike | where name like ? |
| NotLike | findByNameNotLike | where name not like ? |
| StartingWith | findByNameStartingWith | where name like ‘?%’ |
| EndingWith | findByNameEndingWith | where name like ‘%?’ |
| Containing | findByNameContaining | where name like ‘%?%’ |
| OrderBy | findByIdOrderByXDesc | where id=? order by x desc |
| Not | findByNameNot | where name <> ? |
| In | findByIdIn(Collection<?> c) | where id in (?) |
| NotIn | findByIdNotIn(Collection<?> c) | where id not in (?) |
| True | findByAaaTrue | where aaa = true |
| False | findByAaaFalse | where aaa = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByAaaTue | where UPPER(name)=UPPER(?) |
| top | findTop10 | top 10/where ROWNUM <=10 |
使用方法
使用时自定义接口继承JpaRepository,传入泛型,第一个参数为要操作的实体类,第二个参数为该实体类的主键类型
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
List<User> findDistinctByUserName(String userName);
User findByUserName(String userName);
}
解析过程
Spring Data JPA框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,比如find,findBy,read,readBy,get,getBy,然后对剩下的部分进行解析。
假设创建如下查询findByCategoryId(),框架在解析该方法时,首先剔除findBy,然后对剩下的属性进行解析,假设查询实体为Spu
1. 先判断categoryId(根据POJO 规范,首字母变为小写)是否为查询实体的一个属性,如果是,则表示根据该属性进行查询;如果没有该属性,继续第二步;
2. 从右往左截取第一个大写字母开头的字符串此处为Id),然后检查剩下的字符串是否为查询实体的一个属性,如果是,则表示根据该属性进行查询;
如果没有该属性,则重复第二步,继续从右往左截取;最后假设user为查询实体的一个属性;
3. 接着处理剩下部分(CategoryId),先判断用户所对应的类型是否有categoryId属性,如果有,则表示该方法最终是根据"Spu.categoryId"的取值进行查询;
否则继续按照步骤2的规则从右往左截取。
4.可能会存在一种特殊情况,比如Spu包含一个categoryId 的属性,也有一个 rootCategoryId属性,此时会存在混淆。可以明确在属性之间加上"_"以显式表达意图,比如“findByRoot_CategoryId()”
特殊参数
可以直接在方法的参数上加入分页或排序的参数,比如:
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Page<User> findByUserName(String userName, Pageable pageable);
List<User> findByUserName(String userName, Sort sort);
}
JPA的@NamedQueries
(1) 在实体类上使用@NamedQuery
@Entity
@Data
@Table(name = "user")
@NoArgsConstructor
@NamedQuery(name = "User.findByID", query = "select t from User t where t.id = ?1")
public class User {
@Id
@Column(nullable = false)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = false)
private String userName;
}
(2) 在自己实现的DAO的Repository接口里面定义一个同名的方法,示例如下:
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByID(Long id);
}
(3) 然后Spring会先找是否有同名的NamedQuery,如果有,那么就不会按照接口定义的方法来解析
使用@Query
在方法上标注@Query来指定本地查询
参数nativeQuery默认为false,当nativeQuery=false时,value参数写的是JPQL,JPQL是用来操作model对象的。
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query(value = "select t from User t where t.userName like %?1%", nativeQuery = false)
List<User> findByName(String userName);
@Query(value = "select * from user where user_name like %?1", nativeQuery = true)
List<User> findByUser(String userName);
}
nativeQuery=true时,value参数写的是原生sql。
使用@Param命名化参数
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
@Query(value = "select t from User t where t.userName like %?1%", nativeQuery = false)
List<User> findByName(String userName);
@Query(value = "select * from user where user_name like %?1", nativeQuery = true)
List<User> findByUser(String userName);
@Query(value = "select t from User t where t.userName like %:userName%", nativeQuery = false)
List<User> findByNameParam(@Param("userName")String userName);
}
JpaSpecificationExecutor
提供多条件查询。
这个接口比较特殊,单独存在,没有继承以上接口。主要提供了多条件查询的支持,并且可以在查询中添加分页和排序。因为这个接口单独存在,因此需要配合以上说的接口使用。
QueryByExampleExecutor
JPA常用注解
@Entity 注解 - OpenJPA 教程 (hxstrive.com)
@Entity
用于类上面,用来指定该类是一个实体。